Building a University Database with SQL
Introduction
This tutorial guides you through designing, implementing, and understanding a simple university database system. You'll learn how to create tables for students, courses, and enrollments, populate them with sample data, run key queries with explanations and expected results, and visualize the schema with an ER diagram.
1. Database Schema Design
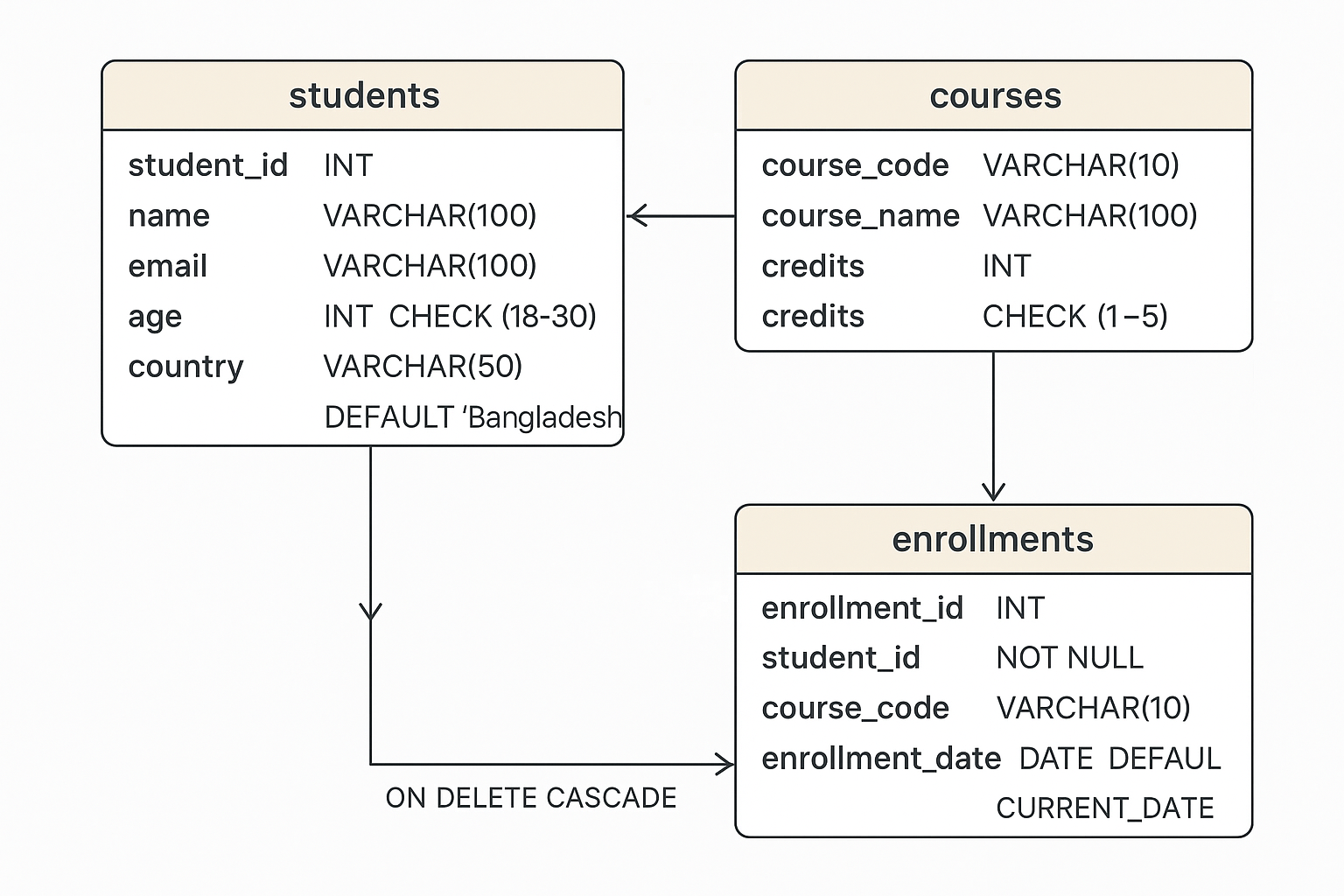
Entities and Their Attributes
- Students
- student_id (Primary Key)
- name (Not Null)
- email (Unique)
- age (Between 18 and 30)
- country (Defaults to 'Bangladesh')
- Courses
- course_code (Primary Key)
- course_name (Not Null)
- credits (Between 1 and 5)
- Enrollments
- enrollment_id (Primary Key)
- student_id (Foreign Key to Students)
- course_code (Foreign Key to Courses)
- enrollment_date (Defaults to current date)

>

2. Creating the Database Tables
-- Create Students table
CREATE TABLE students (
student_id INT PRIMARY KEY,
name VARCHAR(100) NOT NULL,
email VARCHAR(100) UNIQUE,
age INT CHECK (age BETWEEN 18 AND 30),
country VARCHAR(50) DEFAULT 'Bangladesh'
);
-- Create Courses table
CREATE TABLE courses (
course_code VARCHAR(10) PRIMARY KEY,
course_name VARCHAR(100) NOT NULL,
credits INT CHECK (credits BETWEEN 1 AND 5)
);
-- Create Enrollments table
CREATE TABLE enrollments (
enrollment_id INT PRIMARY KEY,
student_id INT NOT NULL,
course_code VARCHAR(10) NOT NULL,
enrollment_date DATE DEFAULT CURRENT_DATE,
FOREIGN KEY (student_id) REFERENCES students(student_id) ON DELETE CASCADE,
FOREIGN KEY (course_code) REFERENCES courses(course_code) ON DELETE CASCADE
);
3. Inserting Sample Data
-- Insert students
INSERT INTO students (student_id, name, email, age, country) VALUES
(1, 'Ahmed', 'ahmed@example.com', 20, 'Bangladesh'),
(2, 'Farzana', 'farzana@example.com', 22, DEFAULT),
(3, 'Md. Rakib', 'rakib@example.com', 19, 'Bangladesh');
-- Insert courses
INSERT INTO courses (course_code, course_name, credits) VALUES
('CS101', 'Introduction to Computer Science', 3),
('MATH201', 'Calculus II', 4),
('ENG105', 'English Literature', 2);
-- Insert enrollments
INSERT INTO enrollments (enrollment_id, student_id, course_code) VALUES
(1001, 1, 'CS101'),
(1002, 1, 'MATH201'),
(1003, 2, 'CS101'),
(1004, 3, 'ENG105');
4. Running and Understanding Key Queries
a) List all students with their enrolled courses
SELECT s.student_id, s.name, c.course_code, c.course_name
FROM students s
JOIN enrollments e ON s.student_id = e.student_id
JOIN courses c ON e.course_code = c.course_code
ORDER BY s.student_id;
Explanation:
This query joins the students, enrollments, and courses tables to display each student's enrolled courses. The results are ordered by student ID for easy reading.
Expected Output:
| student_id | name | course_code | course_name |
|---|
কোন মন্তব্য নেই:
একটি মন্তব্য পোস্ট করুন